오늘은 원래 Terraform을 사용해서 AWS Instance의 생성만 테스트 해 보려고 했다.
근데 하다보니까 튜토리얼이 간단해서인지 금방 끝나서 생성 뿐만 아니라 수정과 삭제도 함께 테스트 해 보았다.
Terraform을 사용 해 AWS에서 인프라를 생성/수정/삭제 하기 위해서는 먼저 AWS CLI가 설치되어 있어야 한다.
AWS CLI는 여기를 참고 해 설치할 수 있다.
0. AWS Access Key 발급
설치 후에는 CLI를 사용하기 위해 Access Key를 발급 받아야 한다.
Access Key는 오른쪽 상단 ID 클릭 > 보안 자격 증명 선택 > 중간의 액세스 키(액세스 키 ID 및 비밀 액세스 키) 선택 > 새 액세스 키 만들기로 생성할 수 있다.
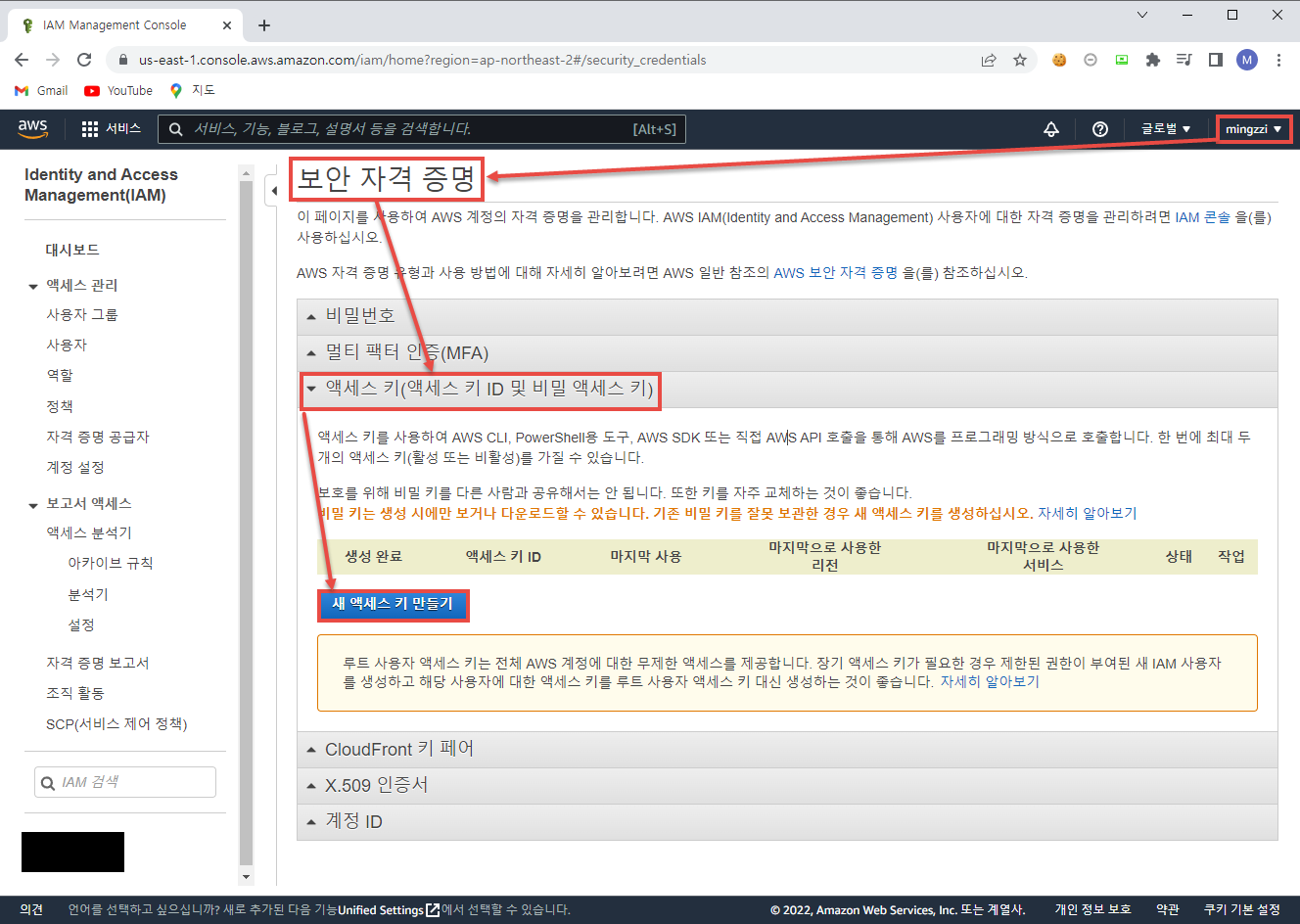
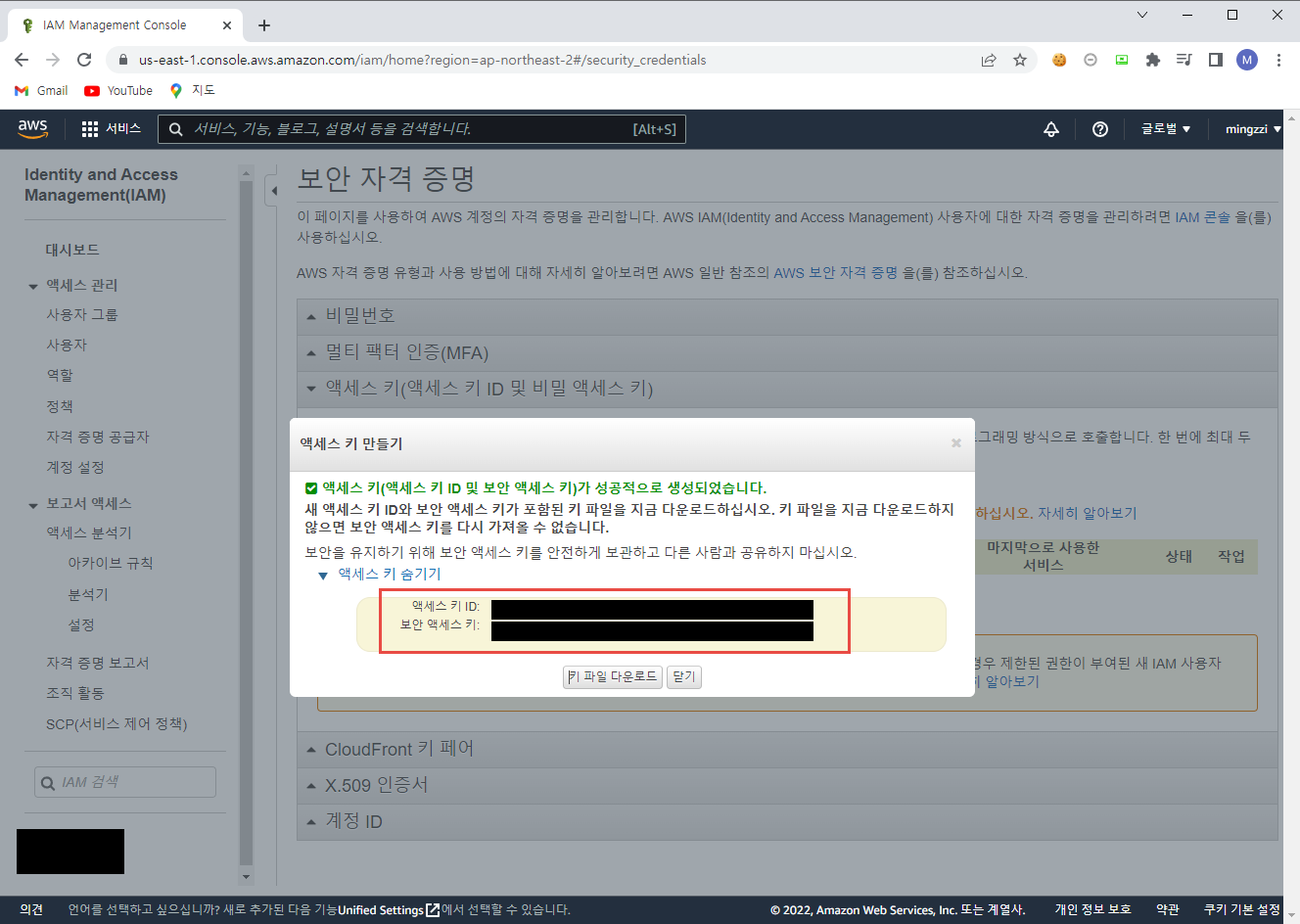
Access Key를 발급 받았다면 Terraform이 설치 된 서버에서 aws configure을 통해 아래와 같이 등록 해 주어야 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
| $ aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]: [AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID]
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: [AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY]
Default region name [None]:
Default output format [None]:
|
1. AWS Instance 생성
이제 AWS를 사용하기 위한 사전 준비는 모두 끝이 났다.
첫 번째 튜토리얼과 같이 새로운 폴더를 하나 생성하여 아래와 같이 main.tf를 작성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| # main.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.16"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.2.0"
}
provider "aws" {
region = "us-west-2"
}
resource "aws_instance" "app_server" {
ami = "ami-830c94e3"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
tags = {
Name = "ExampleAppServerInstance"
}
}
|
각 파트의 설명은 아래와 같다.
Teraform Block
- Terraform이 인프라를 프로비저닝 할 때 사용할 필수 provider 등의 설정
- 각 provider에 대하여 호스트명, 네임스페이스, provider 유형 정의 가능
- Terraform registry에서 provider를 설치 함 (https://registry.terraform.io/)
- 위 예제의 경우 provider의 소스는 registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/aws 의 약자인 hashcorp/aws로 정의
- required_providers 에서 특정 버전 선택 가능 (Optional이며, 선택하지 않을 경우 가장 최신 버전으로 설치)
Providers Block
- 특정 provider를 설정 (위 예제의 경우 aws)
- provider는 Terraform이 리소스를 생성하고 관리하는 데 사용하는 플러그인
- 각각 다른 provider의 리소를 관리하기 위해 여러 개의 provider block을 사용 할 수도 있으며, 서로 다른 provider를 함께 사용하는 것도 가능
Resources Block
- 인프라의 구성 요소 정의
- Resource는 EC2 Instance와 같이 물리적 혹은 가상의 구성 요소일 수 있으며, Heroku 애플리케이션과 같이 논리적 리소스일 수도 있음
- Resource Block에는 리소스의 타입(위 예제의 경우 aws_instance)과 리소스 이름(위 예제의 경우 app_server), 2 개의 문자열이 들어 감
- 리소스 타입의 prefix는 provider와 매핑
- 리소스 타입과 리소스 이름을 조합하여 해당 리소스의 Unique ID로 사용 (위 예제의 경우 ID는 aws_instance.app_server)
- Resources Block에는 리소스를 설정하기 위한 매개변수 들이 포함(머신의 크기, 디스크 이름 이미지 등)
- 위 예제의 경우 매개변수로 AMI ID와 인스턴스 타입을 지정
새로운 설정을 생성했을 경우 terraform init을 통해 configuration directory를 initializing을 해야 한다.
initializing을 할 경우 설정 내 정의 된 provider를 다운받아 설치하게 된다.
위 예제의 경우 aws를 다운 및 설치한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| $ terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Finding hashicorp/aws versions matching "~> 4.16"...
- Installing hashicorp/aws v4.17.1...
- Installed hashicorp/aws v4.17.1 (signed by HashiCorp)
Terraform has created a lock file .terraform.lock.hcl to record the provider
selections it made above. Include this file in your version control repository
so that Terraform can guarantee to make the same selections by default when
you run "terraform init" in the future.
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
|
위 결과 중 3번째 줄을 보면 Initializing provider plugins...라는 부분이 있는데, 해당 부분에서 내가 main.tf에 정의 한 버전인 4.16 이상 버전을 찾는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
그 결과 aws 4.17.1을 설치 완료했다.
이제 terraform apply 명령어를 실행하면 아래와 같이 terraform에서 내 AWS 계정에 EC2 Instance를 생성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
| $ terraform apply
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# aws_instance.app_server will be created
+ resource "aws_instance" "app_server" {
+ ami = "ami-830c94e3"
+ arn = (known after apply)
+ associate_public_ip_address = (known after apply)
+ availability_zone = (known after apply)
+ cpu_core_count = (known after apply)
+ cpu_threads_per_core = (known after apply)
+ disable_api_termination = (known after apply)
+ ebs_optimized = (known after apply)
+ get_password_data = false
+ host_id = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ instance_initiated_shutdown_behavior = (known after apply)
+ instance_state = (known after apply)
+ instance_type = "t2.micro"
+ ipv6_address_count = (known after apply)
+ ipv6_addresses = (known after apply)
+ key_name = (known after apply)
+ monitoring = (known after apply)
+ outpost_arn = (known after apply)
+ password_data = (known after apply)
+ placement_group = (known after apply)
+ placement_partition_number = (known after apply)
+ primary_network_interface_id = (known after apply)
+ private_dns = (known after apply)
+ private_ip = (known after apply)
+ public_dns = (known after apply)
+ public_ip = (known after apply)
+ secondary_private_ips = (known after apply)
+ security_groups = (known after apply)
+ source_dest_check = true
+ subnet_id = (known after apply)
+ tags = {
+ "Name" = "ExampleAppServerInstance"
}
+ tags_all = {
+ "Name" = "ExampleAppServerInstance"
}
+ tenancy = (known after apply)
+ user_data = (known after apply)
+ user_data_base64 = (known after apply)
+ user_data_replace_on_change = false
+ vpc_security_group_ids = (known after apply)
+ capacity_reservation_specification {
+ capacity_reservation_preference = (known after apply)
+ capacity_reservation_target {
+ capacity_reservation_id = (known after apply)
+ capacity_reservation_resource_group_arn = (known after apply)
}
}
+ ebs_block_device {
+ delete_on_termination = (known after apply)
+ device_name = (known after apply)
+ encrypted = (known after apply)
+ iops = (known after apply)
+ kms_key_id = (known after apply)
+ snapshot_id = (known after apply)
+ tags = (known after apply)
+ throughput = (known after apply)
+ volume_id = (known after apply)
+ volume_size = (known after apply)
+ volume_type = (known after apply)
}
+ enclave_options {
+ enabled = (known after apply)
}
+ ephemeral_block_device {
+ device_name = (known after apply)
+ no_device = (known after apply)
+ virtual_name = (known after apply)
}
+ maintenance_options {
+ auto_recovery = (known after apply)
}
+ metadata_options {
+ http_endpoint = (known after apply)
+ http_put_response_hop_limit = (known after apply)
+ http_tokens = (known after apply)
+ instance_metadata_tags = (known after apply)
}
+ network_interface {
+ delete_on_termination = (known after apply)
+ device_index = (known after apply)
+ network_card_index = (known after apply)
+ network_interface_id = (known after apply)
}
+ root_block_device {
+ delete_on_termination = (known after apply)
+ device_name = (known after apply)
+ encrypted = (known after apply)
+ iops = (known after apply)
+ kms_key_id = (known after apply)
+ tags = (known after apply)
+ throughput = (known after apply)
+ volume_id = (known after apply)
+ volume_size = (known after apply)
+ volume_type = (known after apply)
}
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
aws_instance.app_server: Creating...
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [20s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [30s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [40s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [50s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [1m0s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [1m10s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [1m20s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Creation complete after 1m25s [id=i-xxxxxxxx]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
|
+ resource "aws_instance" "app_server"는 "aws_instance" "app_server" 리소스를 추가(+) 하겠다는 의미이며 그 아래에 생성 할 리소스의 정보를 확인할 수 있다.
(known after apply)는 리소스가 생성 될 때까지 알 수 없다는 의미이다.
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy. 부분에서 apply의 결과 어떤 변화가 나타날 지 확인할 수 있고, Enter a value: 옆에 yes를 입력 해 주면 액션을 실행한다.
액션 실행 결과는 마지막 줄의 Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.로 확인할 수 있다.
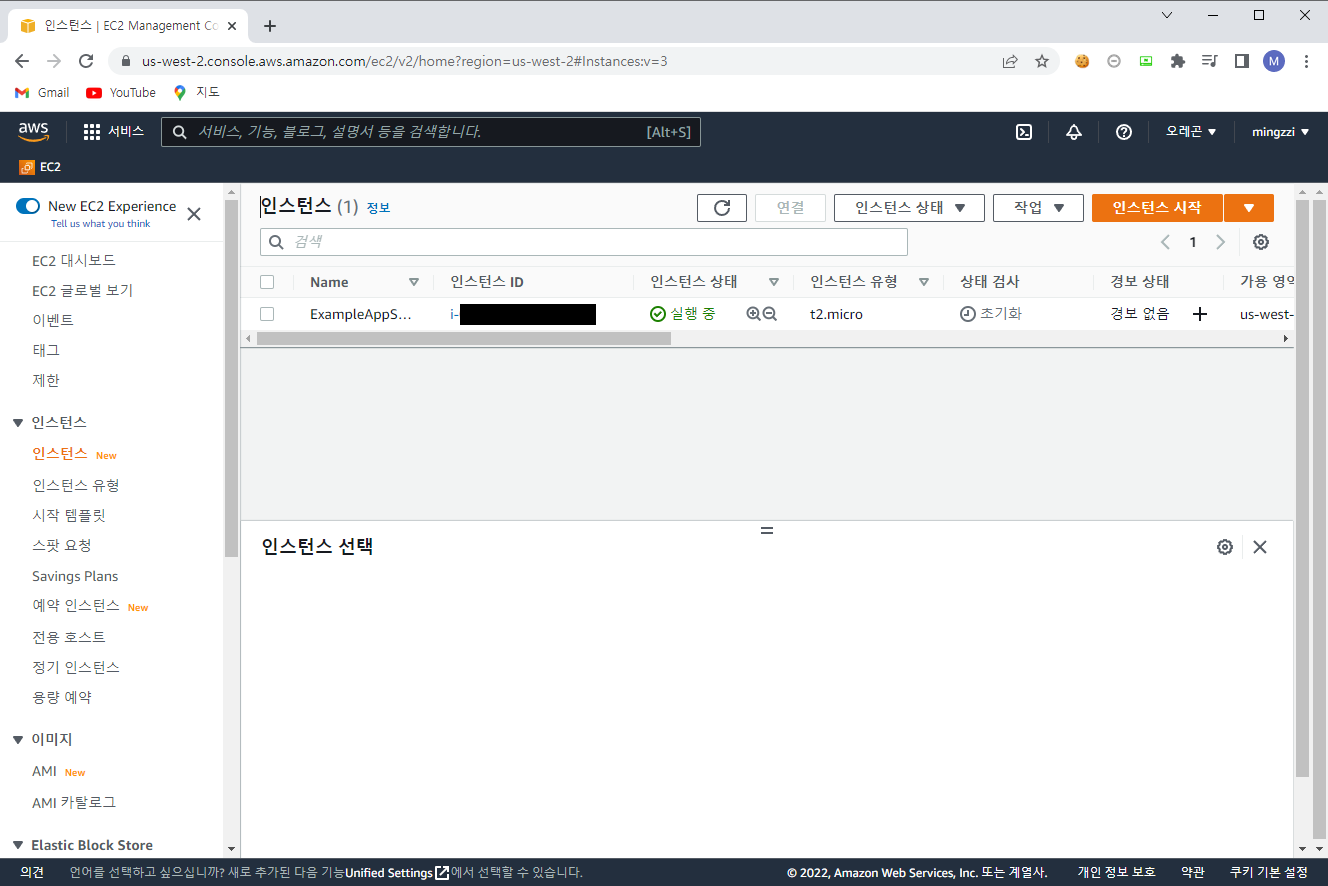
실행 후 AWS 콘솔에 들어 가 보면 아래와 같이 인스턴스가 정상적으로 생성 된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
2. AWS Instance 수정
인스턴스 생성 후 여러 이유로 인스턴스를 변경해야 할 일이 있을 수 있다.
이번에는 생성 한 인스턴스를 수정하는 방법을 확인 해 보려 한다.
앞서 작성 한 main.tf에서 ami 부분을 아래와 같이 수정한다.
1
2
3
4
5
| resource "aws_instance" "app_server" {
- ami = "ami-830c94e3"
+ ami = "ami-08d70e59c07c61a3a"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
}
|
AMI(Amazon Machine Image)는 쉽게 말해 인스턴스 템플릿이다.
OS, Application Server, Application 등이 미리 정의되어 있으며, 내가 필요 한 AMI를 활용하여 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있다.
AMI의 정보는 EC2 > AMI > 퍼블릭 이미지 선택하여 확인할 수 있고, 검색 창에서 여러 필터를 활용 해 내가 원하는 AMI를 찾아 AMI ID를 찾을 수 있다.
또한 AMI ID의 경우 각 지역 별로 다르기 때문에 내가 사용 할 지역을 선택 후 검색해야 한다.
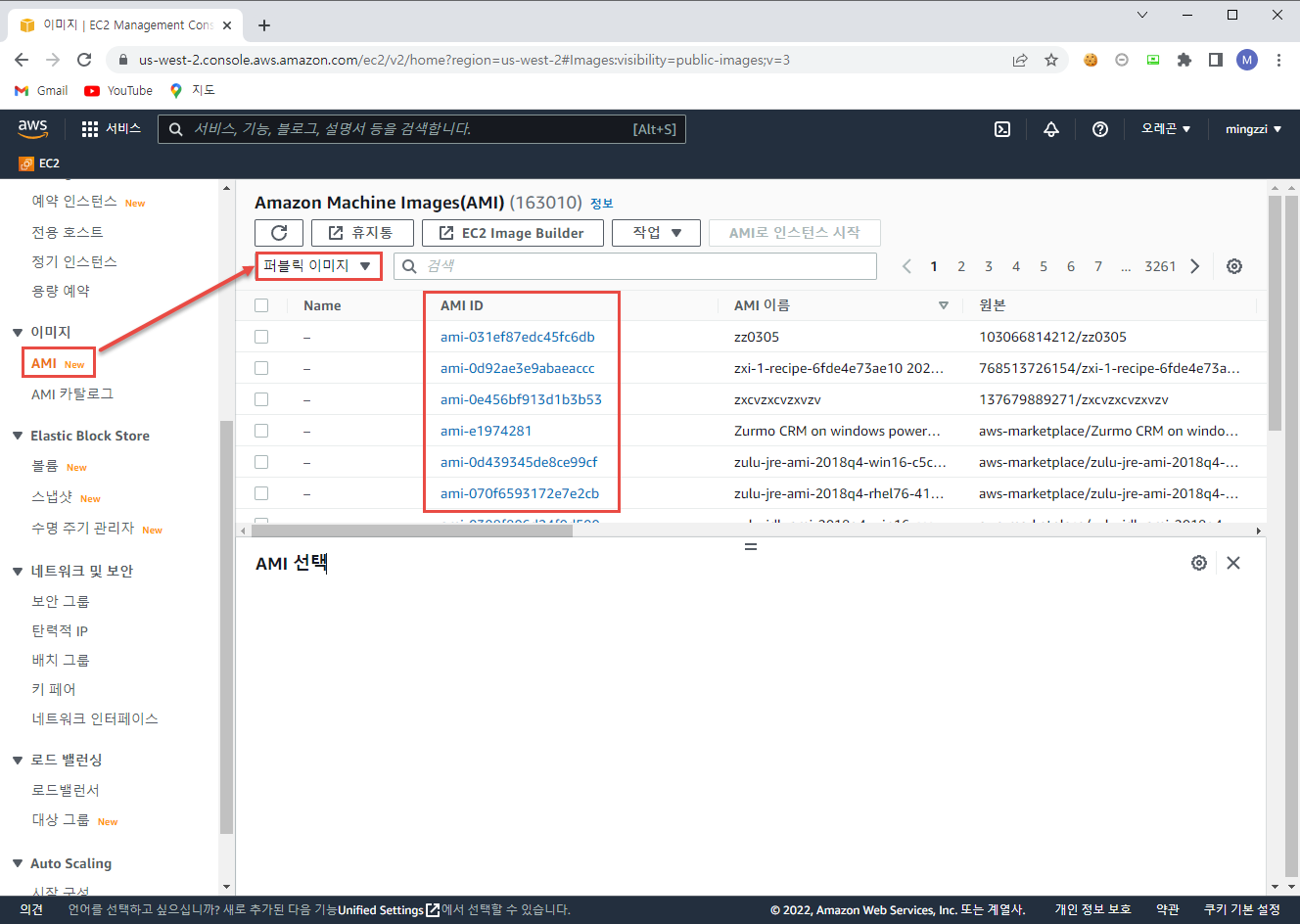
어쨌든 예제에서는 기본에 사용하던 OS를 변경하기 위해 main.tf의 ami를 변경했다.
변경 후 terraform apply를 할 경우 아래와 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
| $ terraform apply
aws_instance.app_server: Refreshing state... [id=i-xxxxxxxx]
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
-/+ destroy and then create replacement
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# aws_instance.app_server must be replaced
-/+ resource "aws_instance" "app_server" {
~ ami = "ami-830c94e3" -> "ami-08d70e59c07c61a3a" # forces replacement
~ arn = "arn:aws:ec2:us-west-2:836940557029:instance/i-xxxxxxxx" -> (known after apply)
~ associate_public_ip_address = true -> (known after apply)
~ availability_zone = "us-west-2c" -> (known after apply)
~ cpu_core_count = 1 -> (known after apply)
~ cpu_threads_per_core = 1 -> (known after apply)
~ disable_api_termination = false -> (known after apply)
~ ebs_optimized = false -> (known after apply)
- hibernation = false -> null
+ host_id = (known after apply)
~ id = "i-xxxxxxxx" -> (known after apply)
~ instance_initiated_shutdown_behavior = "stop" -> (known after apply)
~ instance_state = "running" -> (known after apply)
~ ipv6_address_count = 0 -> (known after apply)
~ ipv6_addresses = [] -> (known after apply)
+ key_name = (known after apply)
~ monitoring = false -> (known after apply)
+ outpost_arn = (known after apply)
+ password_data = (known after apply)
+ placement_group = (known after apply)
+ placement_partition_number = (known after apply)
~ primary_network_interface_id = "eni-xxxxxxxx" -> (known after apply)
~ private_dns = "ip-172-31-6-166.us-west-2.compute.internal" -> (known after apply)
~ private_ip = "172.31.6.166" -> (known after apply)
~ public_dns = "ec2-34-219-42-204.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com" -> (known after apply)
~ public_ip = "34.219.42.204" -> (known after apply)
~ secondary_private_ips = [] -> (known after apply)
~ security_groups = [
- "default",
] -> (known after apply)
~ subnet_id = "subnet-xxxxxxxx" -> (known after apply)
tags = {
"Name" = "ExampleAppServerInstance"
}
~ tenancy = "default" -> (known after apply)
+ user_data = (known after apply)
+ user_data_base64 = (known after apply)
~ vpc_security_group_ids = [
- "sg-xxxxxxxx",
] -> (known after apply)
# (5 unchanged attributes hidden)
~ capacity_reservation_specification {
~ capacity_reservation_preference = "open" -> (known after apply)
+ capacity_reservation_target {
+ capacity_reservation_id = (known after apply)
+ capacity_reservation_resource_group_arn = (known after apply)
}
}
- credit_specification {
- cpu_credits = "standard" -> null
}
+ ebs_block_device {
+ delete_on_termination = (known after apply)
+ device_name = (known after apply)
+ encrypted = (known after apply)
+ iops = (known after apply)
+ kms_key_id = (known after apply)
+ snapshot_id = (known after apply)
+ tags = (known after apply)
+ throughput = (known after apply)
+ volume_id = (known after apply)
+ volume_size = (known after apply)
+ volume_type = (known after apply)
}
~ enclave_options {
~ enabled = false -> (known after apply)
}
+ ephemeral_block_device {
+ device_name = (known after apply)
+ no_device = (known after apply)
+ virtual_name = (known after apply)
}
~ maintenance_options {
~ auto_recovery = "default" -> (known after apply)
}
~ metadata_options {
~ http_endpoint = "enabled" -> (known after apply)
~ http_put_response_hop_limit = 1 -> (known after apply)
~ http_tokens = "optional" -> (known after apply)
~ instance_metadata_tags = "disabled" -> (known after apply)
}
+ network_interface {
+ delete_on_termination = (known after apply)
+ device_index = (known after apply)
+ network_card_index = (known after apply)
+ network_interface_id = (known after apply)
}
~ root_block_device {
~ delete_on_termination = true -> (known after apply)
~ device_name = "/dev/sda1" -> (known after apply)
~ encrypted = false -> (known after apply)
~ iops = 0 -> (known after apply)
+ kms_key_id = (known after apply)
~ tags = {} -> (known after apply)
~ throughput = 0 -> (known after apply)
~ volume_id = "vol-xxxxxxxx" -> (known after apply)
~ volume_size = 8 -> (known after apply)
~ volume_type = "standard" -> (known after apply)
}
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 1 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
aws_instance.app_server: Destroying... [id=i-XXXXXXXX]
aws_instance.app_server: Still destroying... [id=i-XXXXXXXX, 10s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still destroying... [id=i-XXXXXXXX, 20s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still destroying... [id=i-XXXXXXXX, 30s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Destruction complete after 31s
aws_instance.app_server: Creating...
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [20s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [30s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still creating... [40s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Creation complete after 44s [id=i-XXXXXXXX]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 1 destroyed.
|
-/+ resource "aws_instance" "app_server" 부분은 리소스의 추가 및 삭제를 의미하며, 블록 안에서 생성 될 리소스의 정보 및 변경사항을 확인할 수 있다.
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 1 to destroy. 에서 어떤 결과가 나타날 지 확인할 수 있는데, 위 예제의 경우 인스턴스의 OS를 변경하는 작업이기 때문에 기존 인스턴스를 삭제 후 새로 생성하는 작업을 하게 될 예정이다.
검토가 끝났다면 Enter a value: 옆에 yes를 입력하여 작업을 실행할 수 있다.
그 결과 하단에서 기존 인스턴스 삭제 후 새로운 인스턴스를 생성하는 작업을 완료 한 것을 확인할 수 있다.
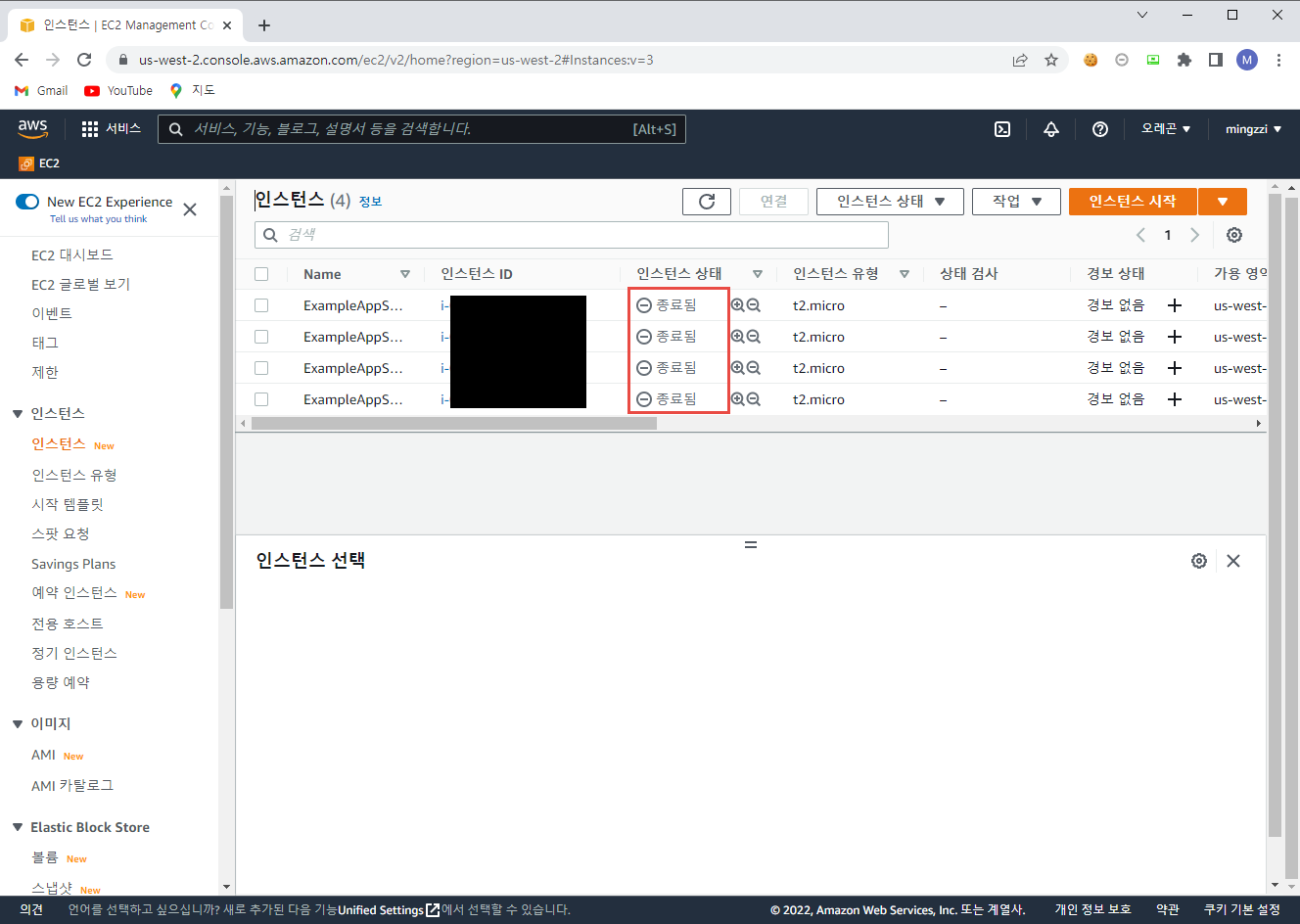
AWS 콘솔에서 확인 결과 아래와 같이 기존 인스턴스 종료 후 새로운 인스턴스가 생성 된 것을 알 수 있다.
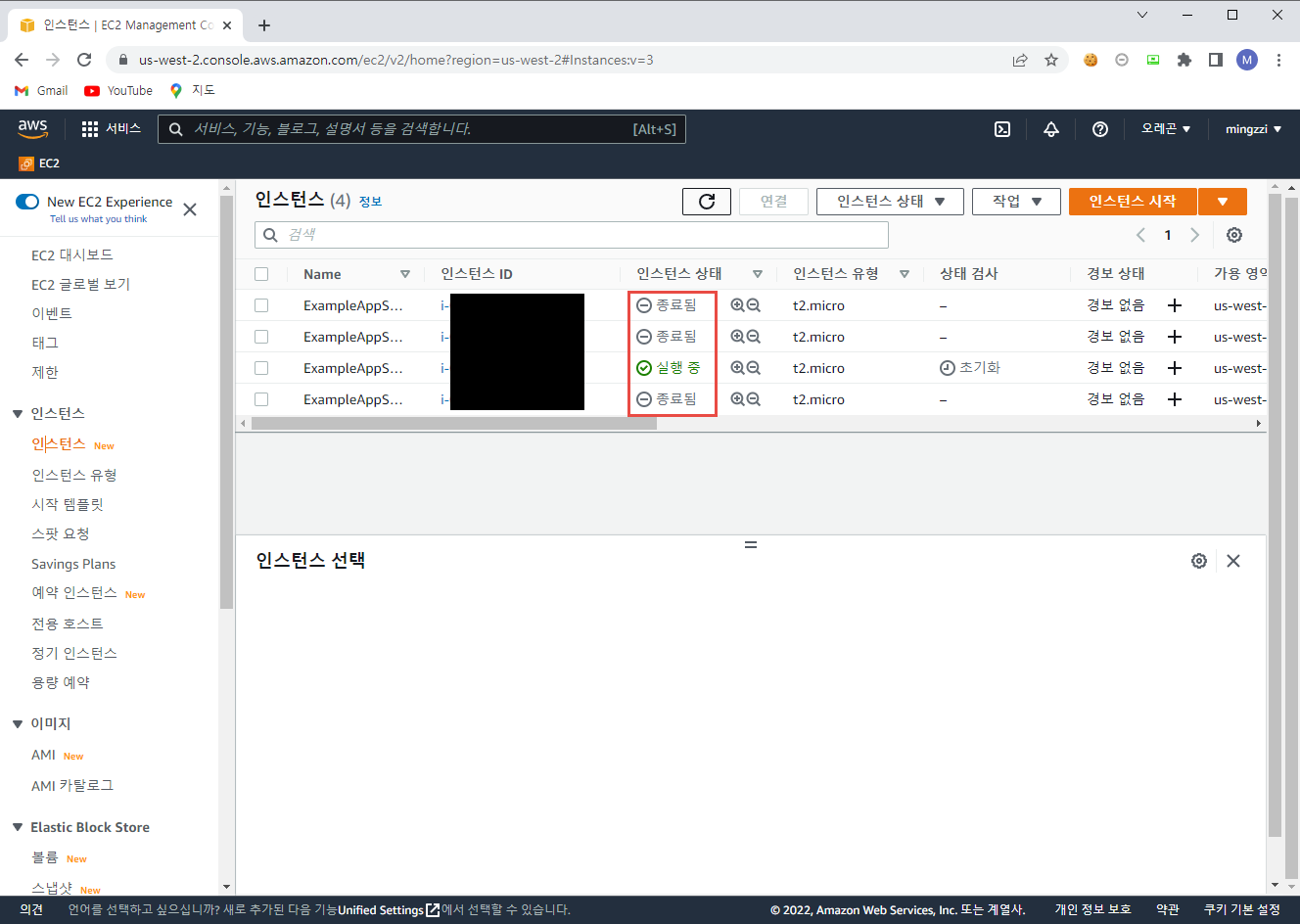
3. AWS Instance 삭제
마지막으로 사용완료 한 인스턴스를 삭제하는 방법이다.
terraform destroy를 사용 할 건데, 이 명령어는 내 terraform 프로젝트 안의 모든 리소스를 삭제하는 명령어로 terraform apply의 반대 역할을 한다.
현재 terraform 프로젝트에 없는 리소스는 삭제 하지 않는다.
사용법은 단순하게 terraform destroy를 입력하면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
| $ terraform destroy
aws_instance.app_server: Refreshing state... [id=i-xxxxxxxx]
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
- destroy
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# aws_instance.app_server will be destroyed
- resource "aws_instance" "app_server" {
- ami = "ami-08d70e59c07c61a3a" -> null
- arn = "arn:aws:ec2:us-west-2:836940557029:instance/i-xxxxxxxx" -> null
- associate_public_ip_address = true -> null
- availability_zone = "us-west-2c" -> null
- cpu_core_count = 1 -> null
- cpu_threads_per_core = 1 -> null
- disable_api_termination = false -> null
- ebs_optimized = false -> null
- get_password_data = false -> null
- hibernation = false -> null
- id = "i-xxxxxxxx" -> null
- instance_initiated_shutdown_behavior = "stop" -> null
- instance_state = "running" -> null
- instance_type = "t2.micro" -> null
- ipv6_address_count = 0 -> null
- ipv6_addresses = [] -> null
- monitoring = false -> null
- primary_network_interface_id = "eni-xxxxxxxx" -> null
- private_dns = "ip-172-31-14-53.us-west-2.compute.internal" -> null
- private_ip = "172.31.14.53" -> null
- public_dns = "ec2-52-12-153-104.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com" -> null
- public_ip = "52.12.153.104" -> null
- secondary_private_ips = [] -> null
- security_groups = [
- "default",
] -> null
- source_dest_check = true -> null
- subnet_id = "subnet-xxxxxxxx" -> null
- tags = {
- "Name" = "ExampleAppServerInstance"
} -> null
- tags_all = {
- "Name" = "ExampleAppServerInstance"
} -> null
- tenancy = "default" -> null
- user_data_replace_on_change = false -> null
- vpc_security_group_ids = [
- "sg-xxxxxxxx",
] -> null
- capacity_reservation_specification {
- capacity_reservation_preference = "open" -> null
}
- credit_specification {
- cpu_credits = "standard" -> null
}
- enclave_options {
- enabled = false -> null
}
- maintenance_options {
- auto_recovery = "default" -> null
}
- metadata_options {
- http_endpoint = "enabled" -> null
- http_put_response_hop_limit = 1 -> null
- http_tokens = "optional" -> null
- instance_metadata_tags = "disabled" -> null
}
- root_block_device {
- delete_on_termination = true -> null
- device_name = "/dev/sda1" -> null
- encrypted = false -> null
- iops = 100 -> null
- tags = {} -> null
- throughput = 0 -> null
- volume_id = "vol-xxxxxxxx" -> null
- volume_size = 8 -> null
- volume_type = "gp2" -> null
}
}
Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 1 to destroy.
Do you really want to destroy all resources?
Terraform will destroy all your managed infrastructure, as shown above.
There is no undo. Only 'yes' will be accepted to confirm.
Enter a value: yes
aws_instance.app_server: Destroying... [id=i-xxxxxxxx]
aws_instance.app_server: Still destroying... [id=i-xxxxxxxx, 10s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still destroying... [id=i-xxxxxxxx, 20s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Still destroying... [id=i-xxxxxxxx, 30s elapsed]
aws_instance.app_server: Destruction complete after 30s
Destroy complete! Resources: 1 destroyed.
|
- resource "aws_instance" "app_server"는 리소스가 삭제된다는 의미이며, terraform apply와 동일하게 아래 블록에서 어떤 식으로 변경되는지 확인할 수 있다.
Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 1 to destroy.에서는 작업의 결과를 미리 확인할 수 있고, Enter a value:에서 yes를 입력하면 작업을 시작한다.
그 결과 하단에서 모든 작업이 완료되고 리소스가 삭제되었다는 문구가 나타난다.
AWS 콘솔에서 확인 결과 모든 인스턴스가 정상적으로 종료 된 것을 확인할 수 있다.